Motivation
Visually-situated language concerns multimodal settings where text and vision are intermixed, and the meaning of words or phrases is directly influenced by what is observable or referenced visually. Settings where text is embedded in an image are ubiquitous, ranging from text on street signs, to chryrons on news broadcasts, language embedded in figures or social media images, or non-digitized text sources.
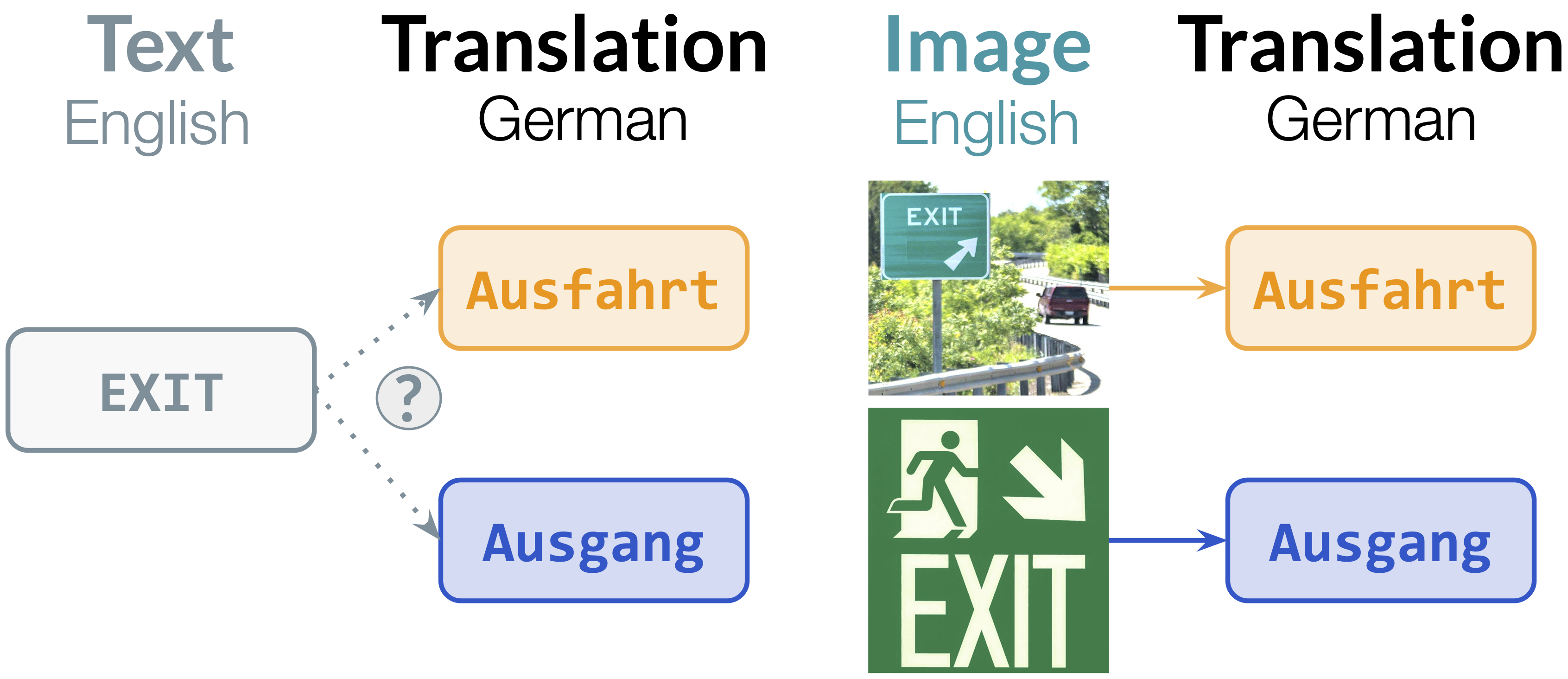
Translating visually-situated text combines a series of traditionally separate steps including text detection, optical character recognition, semantic grouping, and finally machine translation. Not only can errors propagate between steps, as generated mistakes cause mismatches in vocabulary and distribution from those observed in training and reduce downstream task performance, but processing each step in isolation separates recognized text from visual context which may be necessary to produce a correct situational translation. For example, as shown in the example above, the English word 'Exit' can be translated to German as either 'Ausfahrt' or 'Ausgang'; without appropriate context, which may not be present in the text alone, the generated translation would be a statistical guess.
Few public benchmarks exist with images containing text and their translations, necessary to study both the impact of OCR errors on downstream MT, and also to develop and evaluate multimodals to directly translate text in images. We introduce the Vistra benchmark to enable research on this task.
